Quickstart
A typical meltcloud Kubernetes Cluster consists of a Nest-hosted Kubernetes Control Plane and bring-your-own worker nodes called Machines.
TIP
For this Quickstart guide, we'll use the meltcloud SaaS (https://app.meltcloud.io) to host the control planes. For production, you might want to deploy your own Nest on-premises to host the control planes.
Follow these steps to set up a fully managed Kubernetes Cluster with a local VM worker in just a few minutes.
Create a Cluster
- Request a Free Trial for app.meltcloud.io.
- Log in to app.meltcloud.io
- Navigate to Clusters → Create Cluster to create a Cluster by providing a unique name and the Kubernetes version you'd like to use.
- Hit Create Cluster. You can now observe how the control plane is being provisioned by following the operations log:
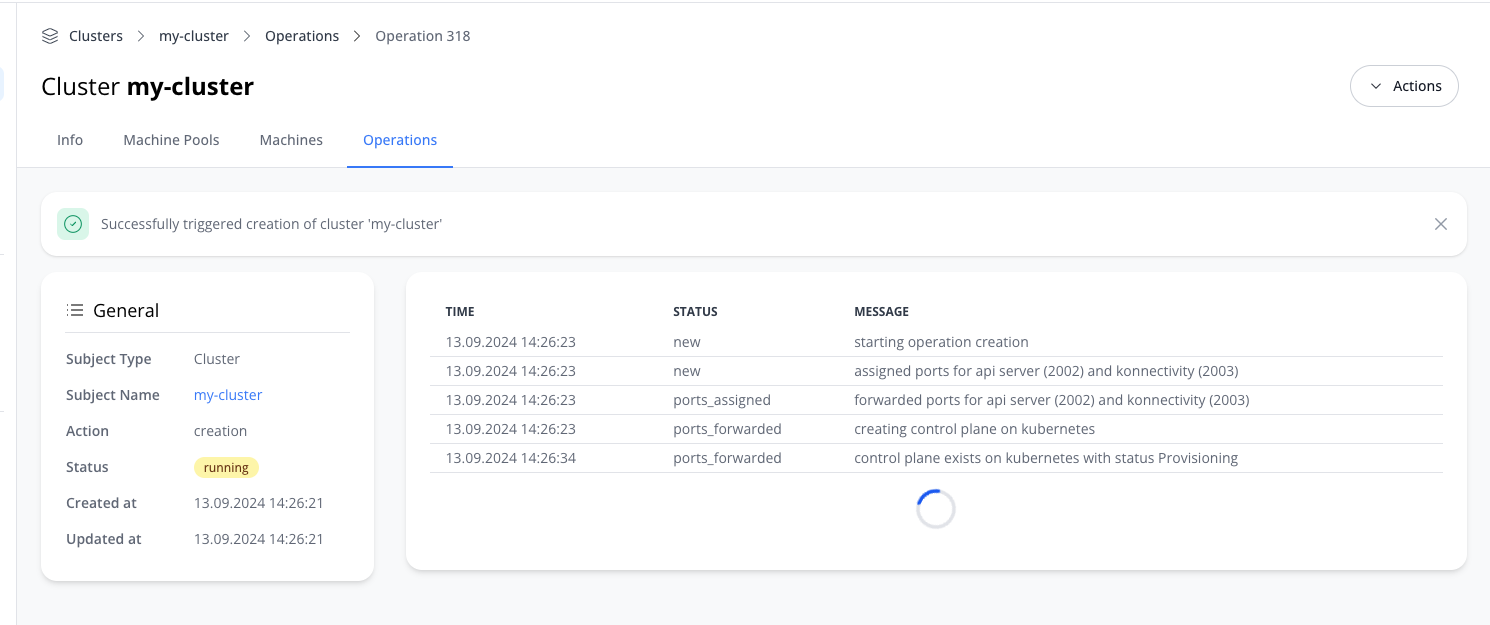
Once your cluster is ready, grab the .kubeconfig (Admin) file from the Info page, which will grant you full access to the cluster.
$ export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/my/cluster.kubeconfig
$ kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes control plane is running at ...
$ kubectl get nodes
# no nodes created yetCreate a Machine Pool
A Machine Pool is used as a grouping entity where you will later assign your Machines to.
Machine Pools share a set of common configuration such as Kubelet version or Network Profiles.
- After the cluster has been created, navigate to the Machine Pools tab in the newly created cluster.
- Choose an appropriate name and leave the default version
- Hit Save Machine Pool.
Create an Enrollment Image
Enrollment Images enable your Machines to securely enroll and join your Kubernetes cluster.
- Follow Create Enrollment Image. Select
/dev/sdaas install disk (QEMU uses that path).
Once finished, download the .iso matching your architecture (amd64 or arm64).
WARNING
Anyone with a valid Enrollment Image might enroll Machines into your organization, so treat it as a secret.
Launch a Virtual Machine with QEMU
Directly launch a virtual machine using QEMU and the previously generated .iso enrollment image.
# install QEMU
brew install qemu
# setup a path to store your QEMU disk files
disks_path=./melt-disks
mkdir -p ${disks_path}
# create a disk for the ephemeral root device that holds docker images
disk_path=${disks_path}/melt-node.qcow2
qemu-img create -f qcow2 $disk_path 20g
# add efi-vars to persist boot order settings
efi_vars=${disks_path}/efi-vars.fd
cp $(brew --prefix qemu)/share/qemu/edk2-arm-vars.fd $efi_vars
# Enrollment Image ISO path - adjust it to your filename
enrollment_iso="$HOME/Downloads/enrollment-image-arm64.iso"
# assign a UUID - be aware that creating a new UUID will create a new machine in meltcloud
machine_uuid=$(uuidgen)
mem=4G # requires at least 4GB - give more for more workload
cpus=6 # no minimum requirement for CPU, but let's give it some power!
# start the machine (Ctrl-a, release, hit x to exit)
qemu-system-aarch64 \
--uuid $machine_uuid \
-m $mem \
-smp $cpus \
-netdev user,id=net1 \
-device nec-usb-xhci,id=usb-bus \
-device usb-storage,drive=meltcloud-iso,removable=true,bus=usb-bus.0 \
-drive if=none,id=meltcloud-iso,media=cdrom,file=${enrollment_iso},readonly=on \
-device virtio-net-pci,netdev=net1,bus=pcie.0,addr=0x19 \
-drive file=$(brew --prefix qemu)/share/qemu/edk2-aarch64-code.fd,if=pflash,format=raw,readonly=on \
-drive file=${efi_vars},if=pflash,format=raw \
-hda ${disk_path} \
-machine virt \
-accel hvf \
-cpu host \
-nographic# install QEMU
sudo apt install qemu-system ovmf
sudo adduser `id -un` kvm
# setup a path to store your QEMU disk files
disks_path=./melt-disks
mkdir -p ${disks_path}
mem=4G # requires at least 4GB
cpus=2
# create a disk for the ephemeral root device that holds docker images
disk_path=${disks_path}/melt-node.qcow2
qemu-img create -f qcow2 $disk_path 20g
# add efi-vars to persist boot order settings
efi_vars=${disks_path}/efi-vars.fd
cp /usr/share/OVMF/OVMF_VARS_4M.fd $efi_vars
# Enrollment Image ISO path - adjust it to your filename
enrollment_iso="$HOME/Downloads/enrollment-image-amd64.iso"
# assign a UUID - be aware that creating a new UUID will create a new machine in meltcloud
machine_uuid=$(uuidgen)
# start the machine (To exit press Alt + 2, then type "quit")
qemu-system-x86_64 \
-uuid $machine_uuid \
-m $mem \
-accel kvm \
-smp $cpus \
-cdrom $enrollment_iso \
-cpu host \
-netdev user,id=hostnet0 \
-device e1000,netdev=hostnet0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x3 \
-drive file=$disk_path,if=virtio \
-drive file=/usr/share/OVMF/OVMF_CODE_4M.fd,if=pflash,format=raw,readonly=on \
-drive file=${efi_vars},if=pflash,format=raw \
-boot order=dLaunch a Virtual Machine using a Desktop GUI
If you rather not fiddle around with QEMU's finicky command line, you can also create a VM in the graphical virtualization tool of your choice (UTM, VirtualBox, VMWare Fusion, ...).
Assign at least 4GB of RAM and 20 GB of disk space to your VM, and ensure boot order is set to the .iso.
WARNING
Be aware that the different virtualization tools use different disk paths (for example VMWare Fusion uses /dev/nvme* path, while UTM/QEMU prefers /dev/sda or /dev/vda).
If the disk path doesn't match the disk path in the Enrollment Image, enrolling will fail (the Enrollment Logs will show the error).
Create another Enrollment Image with the correct disk path for your VM environment to fix this.
Launch
Once the VM boots from the .iso., it wil enroll to meltcloud and reboot once it's finished. It will look as follows:
Troubleshoot
If your VM has trouble booting, check out the Enrollment Images – Troubleshooting section.
Assign the Machine
- After your Machine started up successfully, go to Machines → Your Machine → Actions → Edit Machine and assign it to the Machine Pool you previously created.
Assigning your Machine to a Machine Pool will automatically trigger a reboot and reconfiguration of your Machine.
Verify your cluster
You did it! It's time to verify. Once your Machine reboots, it will automatically join the Kubernetes cluster associated with your Machine Pool.
export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/my/cluster.kubeconfig
kubectl get nodes
# you should see your nodes appear here:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
<some-uuid> Ready <none> 30s v1.33.8The nodes will likely show as NotReady due to the lack of a CNI installation.
For example, to install Cilium as a CNI:
helm repo add cilium https://helm.cilium.io/
helm install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.16.1 \
--namespace kube-system \
--set image.pullPolicy=IfNotPresent \
--set ipam.mode=kubernetesGreat! You now have a meltcloud-managed Kubernetes Cluster with a local VM worker where you could start deploying things.
This environment is fully managed, which means:
- The Control Plane is continuously monitored, scaled and upgraded to the latest patch version.
- The Worker Node is continuously monitored and its software (OS, Kubelet, ...) automatically kept up-to-date.
Curious? As next steps, you could:
- Check out how to enroll an actual Bare Metal Server. Spoiler: It works just as simple as with a VM.
- Want to learn how meltcloud could be set up in your DC? Explore our Platform Overview.
